

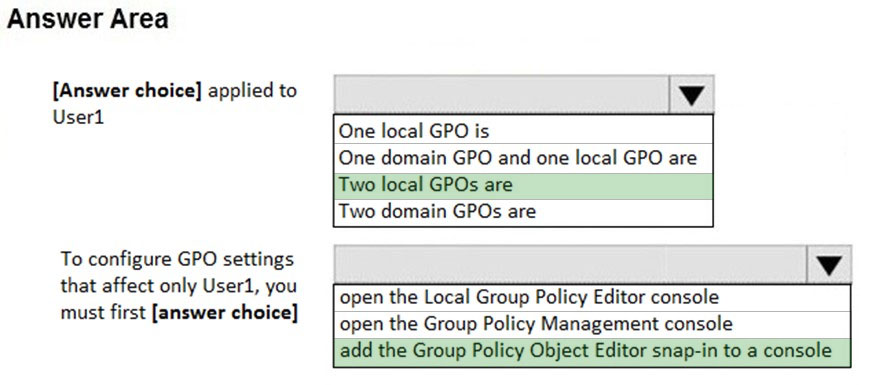
HOTSPOT -
You have a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10.
You are troubleshooting Group Policy objects (GPOs) on Computer1.
You run gpresult /user user1 /v and receive the output shown in the following exhibit.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: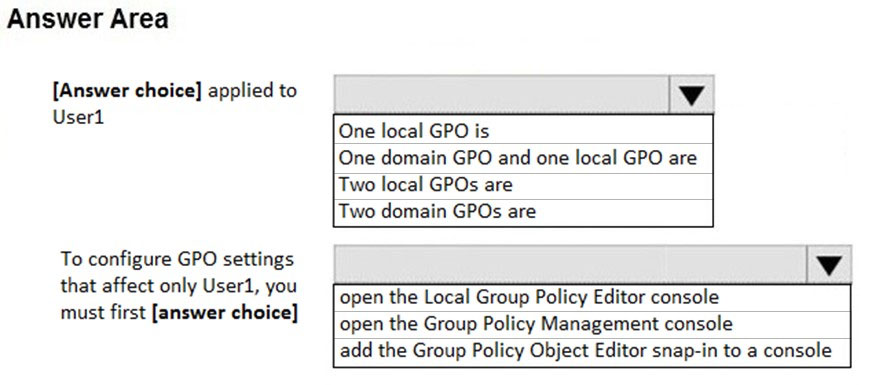
Anthony_2770
Highly Voted 4 years, 9 months agoDivy95
4 years, 8 months agoDuyons
4 years, 8 months agoDnyc
2 years, 6 months agotezawynn
Highly Voted 4 years, 8 months agoflabezerra
Most Recent 2 years, 11 months agoAVP_Riga
4 years, 4 months ago