

Referring to the topology diagram show in the exhibit,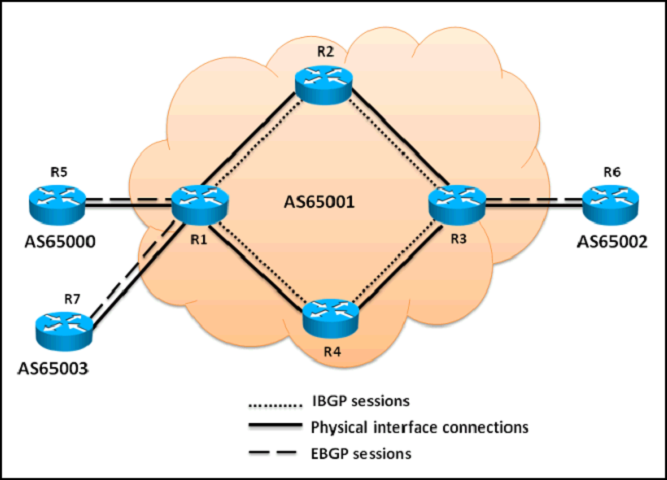
which three statements are correct regarding the BGP routing updates? (Choose three.)
Correct Answer:
ABD
🗳️
When a BGP route reflector receives an IBGP update from a non-client IBGP peer, the route reflector will then forward the IBGP updates to which other router(s)?
Correct Answer:
C
🗳️
Which two BGP mechanisms are used to prevent routing loops when using a design with redundant route reflectors? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AC
🗳️
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios_xr_sw/iosxr_r3.7/routing/configuration/guide/rc37bgp.html
As the iBGP learned routes are reflected, routing information may loop. The route reflector model has the following mechanisms to avoid routing loops:
Originator ID is an optional, nontransitive BGP attribute. It is a 4-byte attributed created by a route reflector.
The attribute carries the router ID of the originator of the route in the local autonomous system. Therefore, if a misconfiguration causes routing information to come back to the originator, the information is ignored.
Cluster-list is an optional, nontransitive BGP attribute. It is a sequence of cluster IDs that the route has passed. When a route reflector reflects a route from its clients to nonclient peers, and vice versa, it appends the local cluster ID to the cluster-list. If the cluster-list is empty, a new cluster-list is created. Using this attribute, a route reflector can identify if routing information is looped back to the same cluster due to misconfiguration. If the local cluster ID is found in the cluster- list, the advertisement is ignored.
Which two statements correctly describe the BGP ttl-security feature? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AD
🗳️
http://packetlife.net/blog/2009/nov/23/understanding-bgp-ttl-security/