

What information would the "beadm list -ds" command output?
Correct Answer:
C
🗳️
You can display information about snapshots, boot environments, and datasets that were created by the beadm command by using the beadm list subcommand.
The beadm list command output also displays boot environments that are created by the pkg command.
The beadm list command syntax is:
Syntax: beadm list [-a | [-ds] [-H] [BeName]
The command lists information about the existing boot environment. To view information for a specific boot environment, replace BeName with a boot environment name. If a specific boot environment is not specified, the command lists information about all boot environments. The default is to list boot environments without additional information.
-a Lists all available information about the boot environment. This information includes subordinate datasets and snapshots.
-d Lists information about all subordinate datasets that belong to the boot environment.
-s Lists information about the snapshots of the boot environment.
-H Prevents listing header information. Each field in the output is separated by a semicolon.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library, Listing Existing Boot Environments and Snapshots
What two entries could complete the following command from the directory listing below?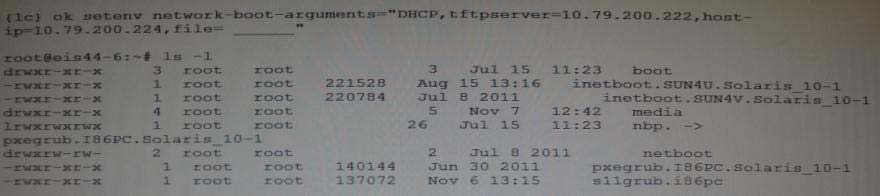
Correct Answer:
DE
🗳️
As per exhibit these are the two files in the netboot directory.
Note:
*Missing argument is:
file=wanbootCGI-URL
Specifies the URL of the wanboot-cgi program on the web server
* During the installation, WAN boot refers to the contents of the /etc/netboot hierarchy on the web server for instructions about how to perform the installation. This directory contains the configuration information, private key, digital certificate, and certificate authority required for a WAN boot installation. During the installation, the wanboot-cgi program converts this information into the WAN boot file system. The wanboot-cgi program then transmits the WAN boot file system to the client.
A developer wants to use DTrace in a zone to examine the kernel. What are his options?
Correct Answer:
C
🗳️
How to Use DTrace in a Non-global Zone
1. Use the zonecfg limitpriv property to add the dtrace_proc and dtrace_user privileges. global# zonecfg -z my-zone zonecfg:my-zone> set limitpriv="default,dtrace_proc,dtrace_user" zonecfg:my-zone> exit
Note -
Depending on your requirements, you can add either privilege, or both privileges.
2. Boot the zone.
3. global# zoneadm -z my-zone boot
Log in to the zone.
global# zlogin my-zone
4. Run the DTrace program.
my-zone# dtrace -l
Note:
* Oracle Solaris DTrace is a comprehensive, advanced tracing tool for troubleshooting systemic problems in real time.
* DTrace helps you understand a software system by enabling you to dynamically modify the operating system kernel and user processes to record additional data that you specify at locations of interest, called probes.
Reference: System Administration Guide: Oracle Solaris Containers-Resource Management and Oracle Solaris Zones, Using DTrace in a Non-Global Zone
Your system has two disk devices, c2t0d0 and c2t1d0, and two flash devices, c2t5d0 and c2t8d0. Which command would you to create a storage pool named
"tank," which mirrors the disks and adds the two flash devices as "cache"?
Correct Answer:
D
🗳️
Creating a ZFS Storage Pool with Cache Devices
You can create a storage pool with cache devices to cache storage pool data. For example:
# zpool create tank mirror c2t0d0 c2t1d0 c2t3d0 cache c2t5d0 c2t8d0
Note:
* Creating a Basic Storage Pool
The following command creates a new pool named tank that consists of the disks c1t0d0 and c1t1d0:
# zpool status tank
pool: tank
state: ONLINE
scrub: none requested
config:
NAME STATE READ WRITE CKSUM
tank ONLINE 0 0 0
mirror-0 ONLINE 0 0 0
c2t0d0 ONLINE 0 0 0
c2t1d0 ONLINE 0 0 0
c2t3d0 ONLINE 0 0 0
cache
c2t5d0 ONLINE 0 0 0
c2t8d0 ONLINE 0 0 0
errors: No known data errors
# zpool create tank c1t0d0 c1t1d0
These whole disks are found in the /dev/dsk directory and are labelled appropriately by ZFS to contain a single, large slice. Data is dynamically striped across both disks.
* Creating a Mirrored Storage Pool
To create a mirrored pool, use the mirror keyword, followed by any number of storage devices that will comprise the mirror. Multiple mirrors can be specified by repeating the mirror keyword on the command line. The following command creates a pool with two, two-way mirrors:
# zpool create tank mirror c1d0 c2d0 mirror c3d0 c4d0
Reference: Solaris ZFS Administration Guide, Creating a ZFS Storage Pool with Cache Devices